Creating an Azure NetApp Files capacity pool using Terraform
In my last post we talked about using Terraform to create an Azure NetApp Files account as well as an Azure Keyvault to support the deployment, you can view that post here. In this post we are going to build on the last one and add an Azure NetApp Files capacity pool to the Terraform code.
Please note, you must have registered your subscription to use the NetApp Resource Provider. For more information on this please have a look at the docs page here.
Hopefully you’ll have a code editor and Terraform installed on your system. If not, to get them installed, whiz on over to this article here.
What are we building today?
Today we will be building the following resources:
- 1 x Resource Group
- 1 x Keyvault
- 1 x Secret
- 1 x Azure NetApp Files account
- 1 x Azure NetApp Files capacity pool
The Terraform code used for this lab can be found in my GitHub here. The files in the repo are used to do the following:
- main.tf – Used to specify providers and create the resource groups
- variables.tf – Used to define variables for this deployment. They are defaults and referenced using the terraform.tfvars file.
- terraform.tfvars – This is file the only file you’ll need to edit amend parameters for your deployment.
- output.tf – This file will be used will be used to capture the randomly generated name of the Resource Group for future deployments that need to reference the name of this resource group.
- keyvault.tf – This file will be used to create the Azure Keyvault and Secret. These will be used in future deployments to specify the username and password for Virtual Machines.
- anf_account.tf – This file is used to create the Azure NetApp Files account.
- anf_capacity_pool.tf – This file is used to create the Azure NetApp Files capacity pool.
Let’s build our Azure NetApp Files capacity pool
In order to create our Azure NetApp File capacity pool, we will require a resource group and and Azure NetApp Files account. This will be done using the following files that we created in previous posts, main.tf and anf_account.tf and are included in this GitHub repo.
1. The code below will be used to create the Azure NetApp Files account in Azure. The Active Directory section has been commented out as some people might not have a requirement for CIFS volumes. If you do have Active Directory within your environment and need to deploy CIFS volumes please uncomment this section and update the .tfvars file as needed.
# Create Azure NetApp Files Account 1
resource "azurerm_netapp_account" "anf_acc_1" {
name = "anf-${var.region_1}-${random_string.rg_random_1.result}"
resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.rg_1.name
location = var.region_1
# Acitve Directory configuration.
# This section has been commented out as an ANF account already exists in my demo subscription and region(s).
# Uncomment this section if you need to add Active Directory configuration and amend the .tfvars file to suit.
/*
active_directory {
username = azurerm_key_vault_secret.admin_secret.name
password = azurerm_key_vault_secret.admin_secret.value
smb_server_name = var.smb_server
dns_servers = [var.dns_server]
domain = var.domain
organizational_unit = var.ou
}
*/
tags = {
Environment = var.tag_environment
CreatedBy = var.tag_createdby
CreatedWith = var.tag_createdwith
Project = var.tag_project
}
}Deploying the code
Once you have your files in your Terraform directory you can go ahead and deploy the code. To do this, open your editor of choice and browse to your Terraform directory.
1. In your Terraform directory, run the following command to initialise the Terraform deployment and download the required modules.
terraform init2. Next we need to create a Terraform plan. This is used to determine what is required to create the configuration you have specified in your Terraform directory. To do this, run the command below.
terraform plan -out main.tfplan3. Now that you have generated your Terraform deployment plan, we can push the Terraform code into Azure and create our resources. Run the command below to apply your code.
terraform apply main.tfplan4. That’s it, you have now deployed your resource group, Keyvault, Azure NetApp Files account and capacity pool. If you have a look in the Azure portal you will see the resource group you created and within it the resources.
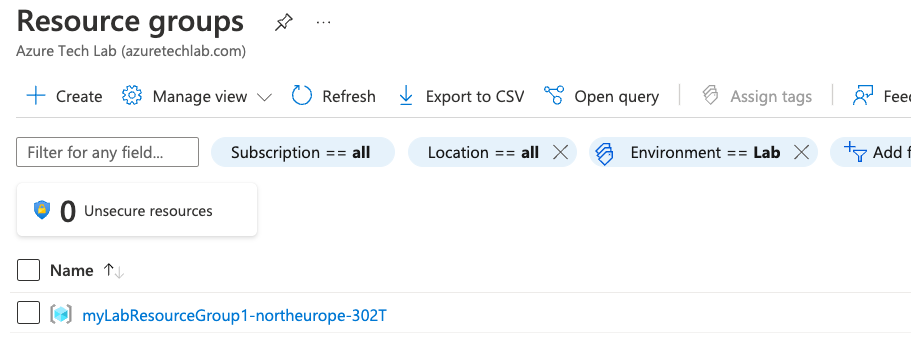
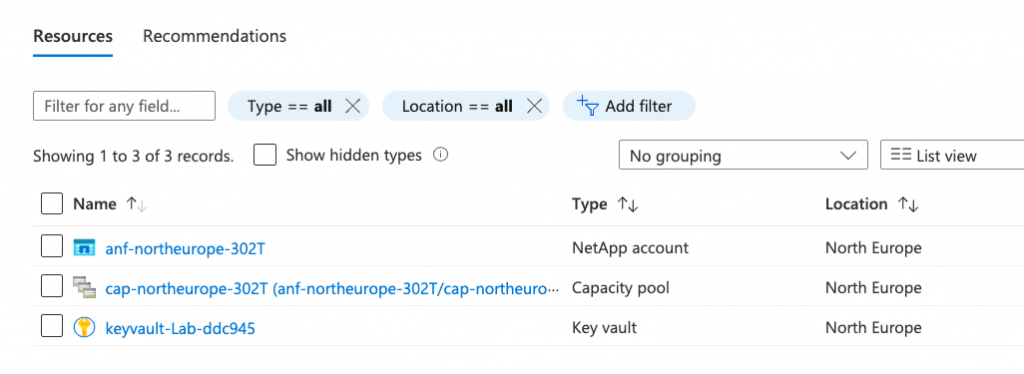
5. Now that you have successfully deployed your resources into Azure, once you have finished with them, it’s time to clean it up and remove your deployment. This is quite straightforward, simply run the command below. This will use the .tfstate file and destroy all resource that terraform built using the apply command previously.
terraform destroySummary
I hope that this very short blog post about creating Azure NetApp Files capacity pools using Terraform has been helpful? I think that the more you use this toolset to deploy infrastructure into Azure, the more you will appreciate its power and simplicity. In my next blog, we’ll build upon this one and add more services into the resource group. Next time, its building Azure NetApp Files Volumes😊